Introduction
Plastic Optical Fibers (POFs) have become an essential component in various industries due to their unique combination of flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and durability. Among these, High-Temperature Resistant Plastic Optical Fiber (HT-POF) stands out for its ability to function effectively under extreme thermal conditions. This article delves into the properties, applications, and recent advancements in HT-POF technology.
Key Properties of High-Temperature Resistant Plastic Optical Fibers
1. Thermal Stability: HT-POFs are engineered to maintain their structural integrity and optical performance at elevated temperatures, typically up to 150°C or higher. This is achieved through advanced polymer formulations that resist thermal degradation.
2. Low Loss Characteristics: These fibers exhibit minimal signal attenuation even in high-temperature environments, ensuring reliable data transmission over long distances.
3. Flexibility and Durability: Despite their heat-resistant properties, HT-POFs remain flexible and resistant to mechanical stress, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
4. Chemical Resistance: Designed to withstand exposure to various chemicals and harsh environments, these fibers are ideal for industrial settings where chemical resistance is critical.
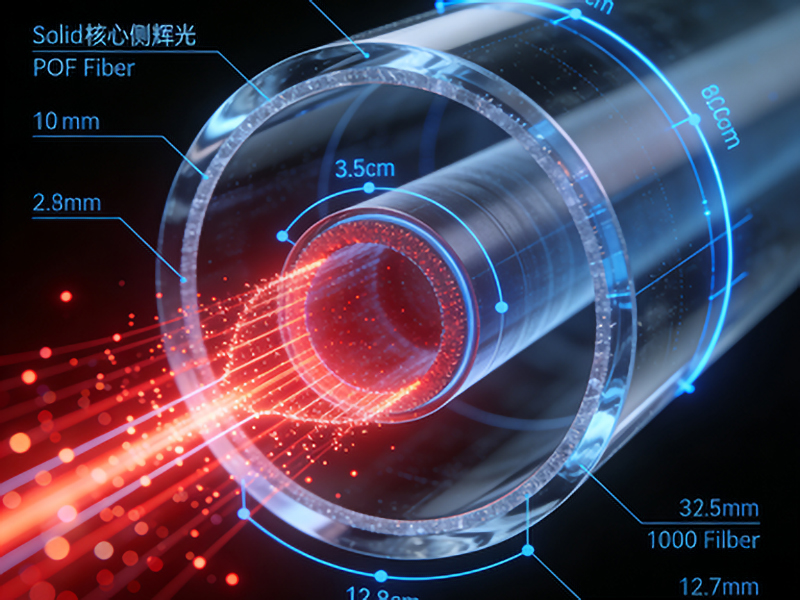
Technical Specifications
– Temperature Range: -40°C to +150°C (typical operating range)
– Attenuation: Less than 0.3 dB/km at the optimal wavelength (usually around 650 nm)
– Diameter: Core diameter of 900 μm or larger for efficient light transmission
– Flexibility Radius: Approximately 20 mm to ensure minimal bending loss
Applications of High-Temperature Resistant Plastic Optical Fibers
1. Industrial Automation: HT-POFs are used in industrial settings for data and signal transmission in harsh environments, such as those involving high temperatures or exposure to chemicals.
2. Telecommunications: In telecommunication networks, these fibers provide reliable connectivity in outdoor installations where temperature fluctuations can be extreme.
3. Automotive Industry: Applications include in-vehicle networking systems, where high temperatures under the hood necessitate robust optical solutions.
4. Oil and Gas Sector: Used in downhole sensing and data transmission in oil wells, where extreme heat and pressure are common.
5. Medical Equipment: HT-POFs find use in medical devices that require sterilization at high temperatures without compromising performance.
Innovations and Future Trends
Recent advancements in material science have led to the development of even more resilient HT-POF materials. Researchers are focusing on improving thermal stability, reducing signal loss, and enhancing mechanical properties. Additionally, the integration of HT-POFs with other technologies like fiber Bragg gratings is opening new possibilities for sensing applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While HT-POFs offer significant advantages, there are challenges to consider:
1. Signal Attenuation: Higher temperatures can lead to increased signal loss, requiring sophisticated compensation techniques or additional repeaters.
2. Cost Considerations: The specialized materials used in HT-POF production make them more expensive than standard POFs.
3. Installation and Maintenance: Proper installation techniques and regular maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance over time.
Conclusion
High-Temperature Resistant Plastic Optical Fiber is a critical technology in addressing the demands of modern industrial, automotive, and telecommunications applications. With ongoing innovations, HT-POFs are expected to play an even more significant role in future optical communication systems.