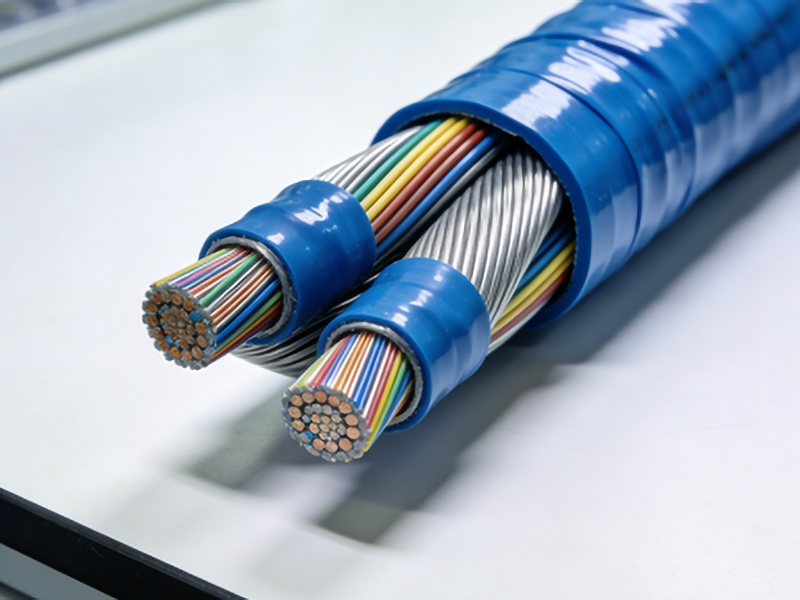
Introduction
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) has emerged as a cost-effective solution for various optical communication needs. Among its variants, Low Noise Plastic Optical Fiber stands out due to its ability to maintain high signal integrity even in noisy environments. This article delves into the technical aspects, applications, and benefits of this innovative technology.
Technical Specifications of Low Noise Plastic Optical Fiber
Low Noise POF is designed with advanced materials that minimize signal degradation caused by external noise. Key technical parameters include:
– Core Diameter: Typically ranges from 50 to 100 microns, optimizing light transmission efficiency.
– Cladding Thickness: Varies between 20 to 40 microns, enhancing the fiber’s durability and flexibility.
– Attenuation Coefficient: Low noise fibers exhibit lower attenuation compared to standard POF, often below 5 dB/km at specific wavelengths.
– Bandwidth: Supports higher bandwidths, making it suitable for high-speed data transmission applications.
Applications of Low Noise Plastic Optical Fiber
The unique properties of low noise POF make it ideal for a variety of applications:
1. Automotive Communication Systems: Used in vehicle networking to ensure reliable and interference-free communication between different modules.
2. Industrial Automation: Employed in industrial settings where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is prevalent, ensuring robust data transmission.
3. Medical Equipment: Applied in medical devices where signal integrity is critical for accurate diagnostics and patient monitoring.
4. Telecommunications: Utilized in local area networks (LANs) to provide high-speed, low-noise connectivity within buildings.
5. Consumer Electronics: Integrated into home entertainment systems and smart devices to enhance performance and reduce interference.
Benefits of Using Low Noise Plastic Optical Fiber
1. Enhanced Signal Integrity: Reduces noise-induced signal loss, ensuring clearer and more accurate data transmission.
2. Cost-Effective Solution: Offers a budget-friendly alternative to traditional glass optical fibers without compromising on performance.
3. Flexibility and Durability: The plastic construction provides greater flexibility and resistance to environmental factors compared to glass fibers.
4. Ease of Installation: Simpler installation process, reducing labor costs and time required for setup.
5. Reduced Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Ideal for environments with high EMI, such as industrial plants or densely populated urban areas.
Challenges and Considerations
While Low Noise POF offers numerous advantages, it also presents some challenges:
– Limited Transmission Distance: Compared to glass fibers, the transmission distance is shorter due to higher attenuation over longer spans.
– Wavelength Limitations: Performance may vary depending on the specific wavelength of light used, requiring careful selection based on application needs.
– Temperature Sensitivity: The plastic material can be more sensitive to temperature fluctuations, potentially affecting performance in extreme conditions.
Conclusion
Low Noise Plastic Optical Fiber represents a significant advancement in optical communication technology. Its ability to maintain signal integrity in noisy environments makes it an invaluable component for various industries. As technology continues to evolve, Low Noise POF is expected to play a pivotal role in meeting the growing demand for reliable and efficient data transmission solutions.




