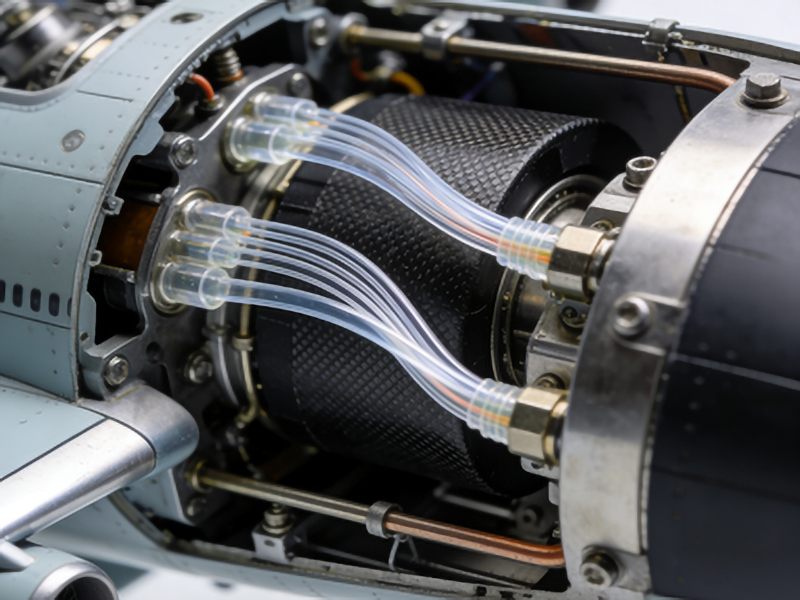
Introduction
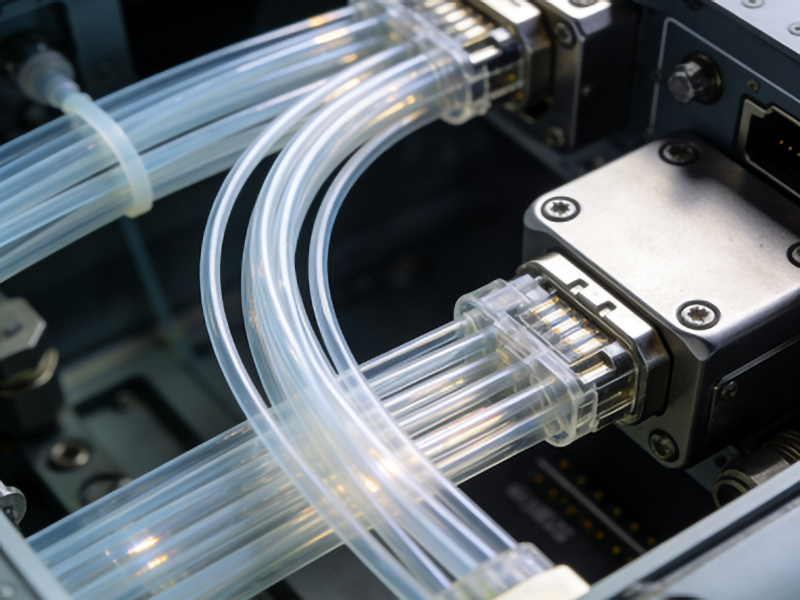
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is revolutionizing the way modern aircraft communicate. Unlike traditional copper wires, POF offers a lightweight, flexible, and highly efficient solution for data transmission within airborne systems. This article delves into how POF is transforming aviation technology, ensuring safer and more reliable communication networks in the skies.
What is Plastic Optical Fiber?
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is a type of optical fiber made from plastic materials, primarily polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). It is designed for short-distance communication applications due to its high transmission loss compared to glass fibers. POF’s flexibility and ease of use make it an ideal choice for various industrial and aviation applications.
Advantages of Plastic Optical Fiber in Airborne Equipment
1. Lightweight Design
POF is significantly lighter than traditional copper cables, reducing the overall weight of aircraft. This reduction contributes to fuel efficiency and extends operational range.
2. Flexibility and Ease of Installation
The flexibility of POF allows it to be easily routed through complex airframes without kinking or damaging the fiber. Its ease of installation reduces maintenance time and costs.
3. Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
POF is immune to electromagnetic interference, which is critical in environments with high levels of EMI, such as aircraft cabins and cockpits. This ensures reliable communication even in electrically noisy environments.
4. High Data Transmission Speeds
Despite being made from plastic, POF supports high data transmission speeds, making it suitable for modern avionics systems that require fast and efficient data transfer.
Technical Parameters of Plastic Optical Fiber
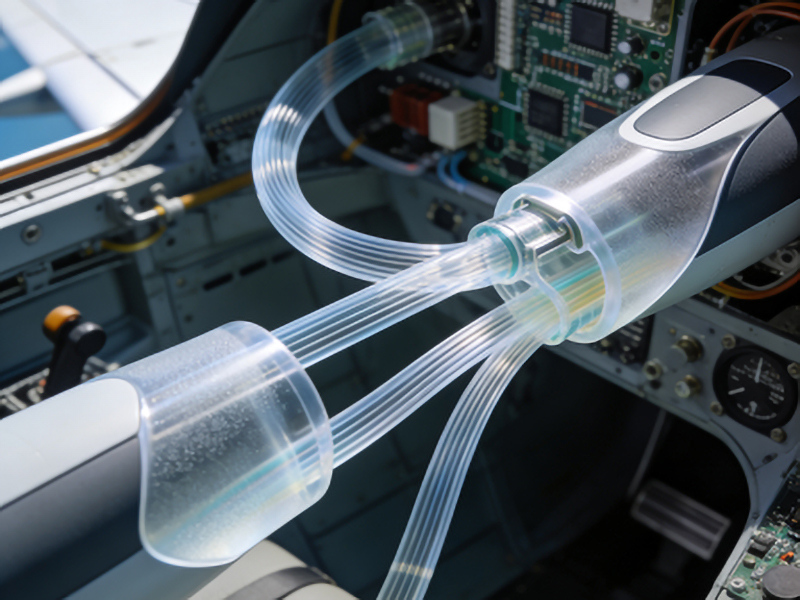
– Core Diameter: Typically ranges from 0.5mm to 1mm, allowing for easier handling and splicing compared to glass fibers.
– Cladding Thickness: Usually between 0.2mm to 0.5mm, providing robust protection against environmental factors.
– Attenuation: Higher than glass fibers, typically around 10 dB/km at 650nm wavelength, limiting its use to short-distance applications.
– Temperature Range: Suitable for operating temperatures from -40°C to +85°C, making it ideal for aviation environments.
Applications in Airborne Equipment
Avionics Systems
POF is used in avionics systems for data transmission between various subsystems, such as flight control computers, navigation systems, and communication devices. Its high-speed capability ensures seamless integration of critical systems.
Passenger Entertainment Systems
In-flight entertainment systems utilize POF to deliver high-quality audio and video content to passengers. The flexibility and lightweight nature of POF make it perfect for routing within cabin interiors.
Sensor Networks
POF is employed in sensor networks to monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration. Its immunity to EMI ensures accurate data transmission even in harsh environments.
Challenges and Limitations
While POF offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations that need consideration:
– Higher Attenuation: Compared to glass fibers, POF experiences higher signal loss over longer distances, restricting its use to short-range applications within aircraft.
– Bandwidth Constraints: Although capable of high-speed data transmission, POF’s bandwidth is limited compared to glass optical fibers, which might be a constraint in future avionics systems requiring ultra-high-speed communication.
Conclusion
Plastic Optical Fiber is playing an increasingly important role in modern airborne equipment. Its lightweight, flexibility, and immunity to EMI make it an ideal solution for various avionics applications. As technology continues to advance, POF will likely become even more integral to the design of next-generation aircraft, ensuring safer and more efficient air travel.
References
1. [Optical Fiber Communication](https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470056320)
2. [Aircraft Avionics Systems](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76382-2)
3. [Plastic Optical Fibers: Properties and Applications](https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/plastic-optical-fiber)