Introduction
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) has long been recognized for its versatility and cost-effectiveness in various applications. With the increasing demand for faster data transmission rates, High-Bandwidth Plastic Optical Fiber (HB-POF) emerges as a groundbreaking solution that combines the benefits of traditional POF with enhanced performance capabilities. This article delves into the technical aspects, advantages, applications, and future prospects of HB-POF.
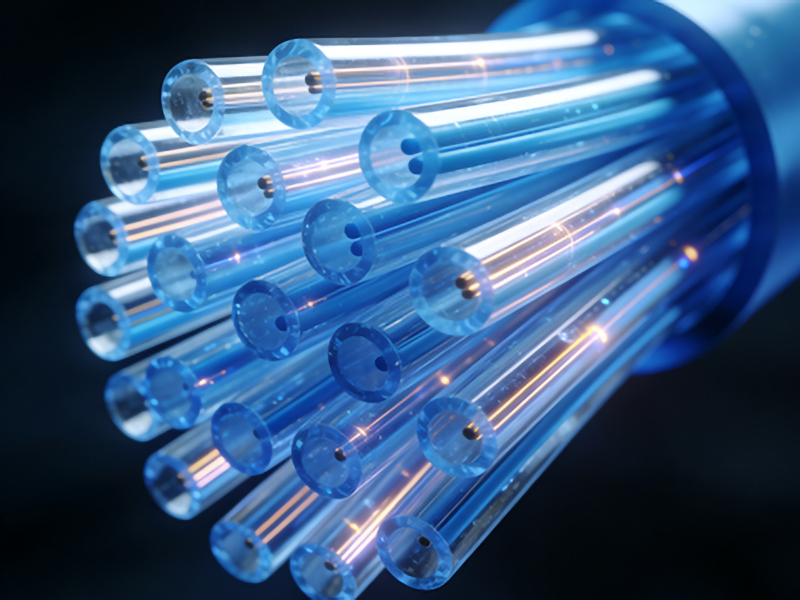
Technical Specifications
High-Bandwidth Plastic Optical Fiber is designed to overcome the limitations of conventional plastic fibers by offering improved bandwidth and data transmission speeds. Key technical parameters include:
– Numerical Aperture (NA): Typically ranging from 0.35 to 0.45, NA determines the fiber’s ability to capture light. A higher NA enhances coupling efficiency but may lead to increased modal dispersion.
– Core Diameter: HB-POF often features a core diameter of around 1 mm, which is significantly larger than traditional POF. This design allows for higher power handling and improved signal integrity over longer distances.
– Cladding Thickness: The cladding layer, usually between 0.25 to 0.35 mm, plays a crucial role in minimizing signal loss and maintaining the fiber’s mechanical integrity.
– Attenuation: HB-POF exhibits lower attenuation compared to standard POF, enabling longer transmission distances without significant signal degradation.
– Modal Bandwidth: With modal bandwidths exceeding 1 GHz·km, HB-POF supports data rates of up to 10 Gbps, making it suitable for high-speed applications.
Advantages of High-Bandwidth Plastic Optical Fiber
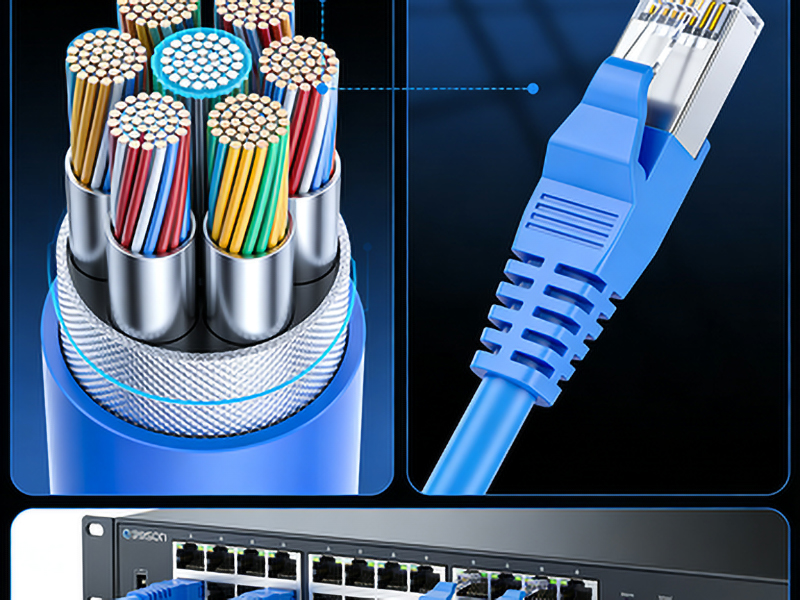

HB-POF offers several advantages that make it an attractive option in the field of optical communication:
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most significant benefits of HB-POF is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to traditional glass-based fibers, HB-POF is significantly cheaper due to the lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes.
Flexibility and Ease of Use
HB-POF is highly flexible and easy to install, making it ideal for applications where frequent reconfiguration or mobility is required. Its large core diameter simplifies coupling, reducing the need for precise alignment during installation.
Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Unlike copper cables, HB-POF is immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable data transmission in environments with high EMI levels.
Lightweight and Durable
HB-POF is lightweight and resistant to harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Its durability ensures long-term reliability without performance degradation over time.
Applications of High-Bandwidth Plastic Optical Fiber
The versatility of HB-POF makes it applicable in a wide range of fields:
Telecommunications
HB-POF is increasingly being adopted in telecommunications for high-speed data transmission within local area networks (LANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs). Its ability to support multi-gigabit speeds ensures efficient data transfer with minimal latency.
Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, HB-POF is used for connecting sensors, actuators, and control systems. Its immunity to EMI and high data transmission rates make it ideal for real-time communication in automation environments.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector benefits from HB-POF’s lightweight and flexibility, using it for in-vehicle networking and data communication between different subsystems. This reduces the overall weight of vehicles while enhancing data transfer efficiency.
Medical Equipment
In medical devices, HB-POF is employed for its high-speed data transmission capabilities and immunity to EMI, ensuring reliable operation in critical healthcare environments.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, HB-POF faces certain challenges:
Limited Transmission Distance
While HB-POF supports higher bandwidths compared to standard POF, it still has a limited transmission distance due to higher attenuation rates when compared to glass fibers. This makes it more suitable for short-range applications.
Modal Dispersion
The larger core diameter of HB-POF can lead to increased modal dispersion, which may affect signal quality over longer distances or at higher data rates.
Future Prospects
As technology continues to evolve, researchers are focusing on improving the performance of HB-POF by developing advanced materials and manufacturing techniques. Potential advancements include:
– Improved Modal Bandwidth: Innovations in fiber design could lead to higher modal bandwidths, enabling even faster data transmission rates.
– Reduced Attenuation: Advances in cladding materials and core compositions aim to minimize signal loss over longer distances.
– Integration with Next-Generation Networks: HB-POF is expected to play a significant role in 5G networks and beyond, providing cost-effective solutions for high-speed data communication.
Conclusion
High-Bandwidth Plastic Optical Fiber represents a promising advancement in optical communication technology. Its combination of high performance, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use makes it an ideal solution for various applications across industries. As research and development continue to push the boundaries of HB-POF capabilities, its role in future telecommunications and data transmission systems is set to grow significantly.





